learn.dev42.co.uk
Network Layers And Protocols
[!IMPORTANT] This Page Is Still A Working Progress.
Network Protocols refer to a set of rules and conventions that define how data is transmitted and received over a network. They establish the methods and procedures for communication between different network devices.
Physical Layer (L1)
Transmission of raw bitstreams over physical mediums.
-
USB (Universal Serial Bus):
-
DSL (Digital subscriber line):
-
ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line)
- 802.11 WiFi (wireless fidelity):
- 802.11
- WiFi 1 Released: 1997 Frequency: 2.4GHz
- 802.11b
- WiFi 2 Released: 1999 Frequency: 2.4GHz
- 802.11a
- Wifi 3 Released: 1999 Frequency: 5GHz
- Released: 2003 Frequency: 2.4GHz
- 802.11g
- WiFi 4 Released: 2009 Frequency: 2.4GHz, 5GHz
- 802.11n
- WiFi 5 Released: 2013 Frequency: 5GHz
- 802.11ac
- WiFi 6 Released: 2021 Frequency: 2.4GHz, 5GHz
- 802.11ax
- WiFi 6E Released: 2024 Frequency: 6GHz
- 802.11be
- WiFi 7 Released: 2024 Frequency: 2.4GHz, 5GHz, 6GHz
- 802.11bn
- WiFI 8 Released: a Frequency: 2.4GHz, 5GHz, 6GHz
- 802.11
- 1000BASE-T
Data Link Layer (L2)
Link Layer Protocols: Protocols that work at the network interface level, facilitating data transfer between devices on the same local network, like Ethernet.
-
MAC (Media Access Control)
-
Ethernet
-
VLan (virtual Local Area Network)
-
VPN (Virtual Private Network)
Network Layer (L3)
Routing data packets through the network.
-
IP (Internet Protocol): Routes one packet from a source machine to a destination machine. IP wraps other higher level protocols such as TCP, UDP, etc, which handle routing packets to a specific application/port on the destination machine.
-
NAT (Network Address Translation)
Transport Layer (L4)
Transport Protocols: Protocols responsible for end-to-end communication, ensuring complete data transfer. Examples include TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol).
-
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): Routes data to a specific port. TCP provides acknowledgements to verify that a packet was recieved by the destination as well as ensures ordering of packets.
-
UDP (User Datagram Protocol): A lightweight protocol that routes a packet to a specific port. UDP does not handle any acknowledgement or ordering of packets.
Session Layer (L5)
Maintaining sessions and controlling connections.
-
SMB
-
RTCP
-
SOCKetS
Presentation Layer (L6)
Translation of data formats and encryption.
-
TLS
-
SSL
Application Layer (L7)
Application Protocols: These protocols provide services directly to end-users and define how applications interact over a network, such as HTTP for web browsing and SMTP for email.
-
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): Used to access web pages.
-
FTP (File Transfer Protocol): Used for transferring files between computers.
-
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure): Encryption and authentication for requesting and sending secure websites using HTML.
-
DHCP
-
DNS
-
NFS
-
POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3): old
-
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): Sends an email to an email server. In the name, its simple and is being retired in September 2025.
-
SNMP
-
NTP
-
IRC
-
SSH
-
IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol): Used by mail clients to manage and remove mail boxes and retrieve emails from there servers.
OSI Model
[!NOTE] We Don’t Need To Know This For GCSE AQA!
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model describes seven layers that computer systems use to communicate over a network. The OSI model is divided into seven distinct layers, each with specific responsibilities, ranging from physical hardware connections to high-level application interactions.
Each layer of the OSI model interacts with the layer directly above and below it, encapsulating and transmitting data in a structured manner. The OSI model serves as a universal language for networking, providing a common ground for different systems to communicate effectively.
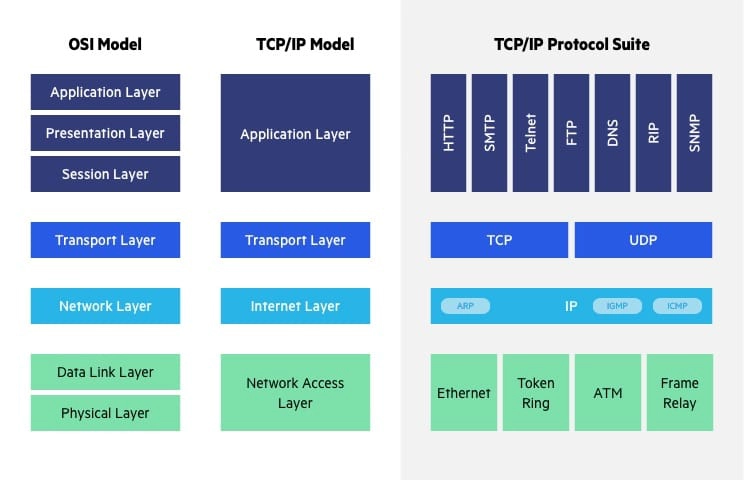
OSI vs. TCP/IP Model
The Transfer Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is older than the OSI model and was created by the US Department of Defense (DoD). A key difference between the models is that TCP/IP is simpler, collapsing several OSI layers into one:
- OSI layers 5, 6, 7 are combined into one Application Layer in TCP/IP
- OSI layers 1, 2 are combined into one Network Access Layer in TCP/IP – however TCP/IP does not take responsibility for sequencing and acknowledgement functions, leaving these to the underlying transport layer.
Other important differences:
- TCP/IP is a functional model designed to solve specific communication problems, and which is based on specific, standard protocols. OSI is a generic, protocol-independent model intended to describe all forms of network communication.
- In TCP/IP, most applications use all the layers, while in OSI simple applications do not use all seven layers. Only layers 1, 2 and 3 are mandatory to enable any data communication.